Digital Inclusion
We believe in Equality, Diversity and Inclusion (EDI)
Some lecturers use teaching examples which are not suitable for a diverse audience coming from different backgrounds. There is a greater need for student equity as the transition to online learning did not affect all student groups equally.
Digital inclusion ensures that the benefits of the internet and digital technologies are available to everyone. This means universities must remove technology barriers for all students, ensuring that everyone has the same learning opportunities as their peers. Our project, therefore, focuses on gaps and improvement in delivering an inclusive digital experience from a student perspective at the University of Westminster.
Our objective as Student Digital Ambassadors (SDA) was to identify ‘Gaps‘ in online learning and digital inclusivity that Westminster students and teaching staff face. We also discuss methods to fill those gaps through technology and training.
Introduction on Digital Inclusion by Opeyemi Yusuf and Shashwat Guha
Gap 1: Discrimination and prejudiced teaching by Shashwat Guha
Opinions and experiences of minority ethnic students are often disregarded during lectures which can have a great impact on their mental health and serve to alienate them in a foreign country. International students like me for example, find it hard to cope with the feelings of loneliness and depression and this is worsened by the online learning experience due to the pandemic.

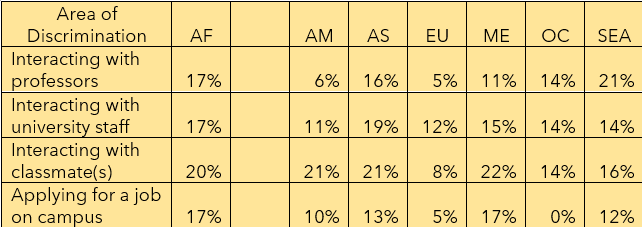
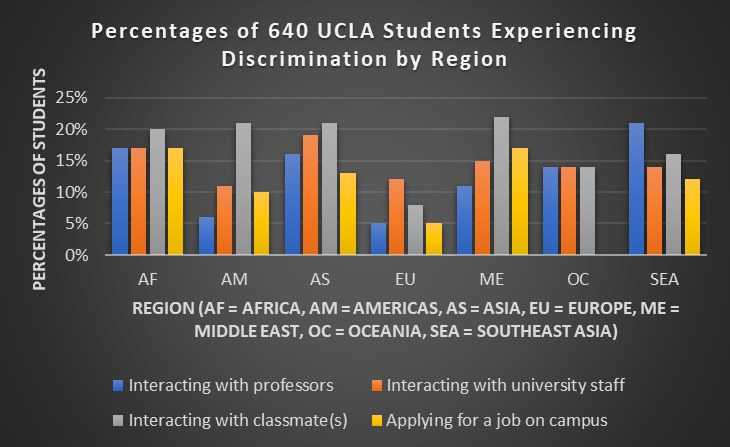
According to Hanassab (2006), international students from Africa, Middle East, Central and South-East Asia, experienced some of the highest levels of discrimination and misguided teaching at University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA). Similar feedback in recent times of unrest, is also prevalent among teaching institutions including University of Westminster. This calls for crucial measures to make
the teaching more inclusive, informed and diverse, starting at the grassroots level partnering with personal tutors and lecturers, all the way to the heads of institutions.
The Attainment Gap – Students from BME backgrounds are 20% less likely to achieve a first or 2:1 degree classification compared to their White counterparts, despite arriving at university with the same grades.
According to Magd (2016), 92.39% of professors in UK academia are white (15,905), with only a minuscule 0.49% being Black (85) and just 17 of those being women. And of those Black academics only 0.58% occupy senior management roles (only 15).
Solutions and future plans to overcome Gap 1
- The University of Harvard Project Implicit – An internationally renowned, valid, test can help identify bias across a number of areas including gender, religion, country of origin, sexual identity and
so on. https://implicit.harvard.edu/implicit/takeatest.html
- Proper EDI training – for professors, students and university staff embedding equity and inclusivity within learning and teaching (Hanassab, 2006). https://www.futurelearn.com/microcredentials/online-teaching-embedding-social-race- and-gender-related-equity
- Greater representation – among higher, more prestigious roles to ensure race equality and decolonising the curriculum (Magd, 2016).
Prejudiced teaching discussion
Prejudiced teaching solutions
Gap 2: Digital Accessibility by Shashwat Guha
Students may often have hidden and/or financial difficulties such as feeling unwell or not being able to afford a laptop or tablet for attending online lectures. Some peers I have spoken to, were worried because they did not know where to go for help in such cases. Some did not even receive timely replies to their emails asking for support and missed out on important lectures.
The environment at home or outside could be too distracting and unsuited for learning. I can definitely attest to this, owing to lack of privacy in an Asian household, noisy construction sounds and pesky partygoers outside at night! International students not living in the same country, also find it difficult to coordinate timings with live lectures and could benefit from high quality recorded material to catch up to their peers. Inadequate digital literacy of certain students due to a lower-income background or unfamiliarity with technology, may render them incapable of dealing with virtual dashboards and tools for resources, exams and assignments.
Unforeseen circumstances such as no stable Wi-Fi connection, or a working mic could also lead to increased student dissatisfaction over digital learning and inclusivity. I have had so many instances where my devices failed when I needed them most during a presentation or lecture!
The lecturers usually do not pause their teaching to accommodate students lagging behind because they are on a strict schedule and may have other commitments. This causes students to lose interest and fall behind in their studies. The teaching staff may also have some false assumptions and lack of sensitivity regarding online learning.

Digital Accessibility Discussion
Solutions and future plans to overcome Gap 2
Speech/audio to text transcription and translation applications using AI and machine learning can be used for lecture recordings
Assumption 1: What is being moved online is a curriculum.
Assumption 2: The challenges of moving online are technical and skills based.
Assumption 3: Changing from on campus to online can be done smoothly, without significant additional time, support, and faculty development.
Assumption 4: The principles of teaching online are somehow different from on campus.
Gap 3: Knowledge Nugget by Opeyemi Yusuf
My focus for this project covers knowledge nugget, its gaps and solution to make it more digital inclusive for students. Knowledge nuggets are bite-size pre-lectures released before the actual lecture on Blackboard. They are a valuable resource to prepare for the lectures, reviewing for missed lectures and exam support. The gaps I researched include issues with accessibility and quality.
Firstly, they tend to consist of short slides with a longer length of time i.e, 2 to 3 slides for a 40-minute lecture. They are usually in black and white fonts with a lack of colour, graphs, or animations to engage students. Moreover, knowledge nugget in some instances feels like the lecturers are reading from a textbook rather than substantial teaching. Lastly, there is an issue with accessibility as students are unable to download the video.
Knowledge Nugget Discussion
The use of 2-3 slides for knowledge nuggets means that students are unable to engage with the slides. this massively affect and exclude non-native english speakers and student with learning disabilities as they will spend longer trying to understand the audio being spoken as there is no written information for the topic. The small font print and style of the presentation mean students with learning difficulties such as Dyslexia are excluded due to difficulties with reading. The result of lack of quality means that student tends to find knowledge nugget boring, unengaging, and difficult to comprehend. Overall detrimental to the digital inclusivity goal of the university and the student itself.

Solutions to overcome Gap 3
Solutions could include creating a guide on inclusive teaching practices for lecturers and students to access easily online or in booklet form. For example, the University of Oxford has a page for inclusive teaching for all students through lectures and guidance for students with learning difficulties. Both staff and students can benefit from this as the lecture would uniformly have a digital inclusive guide to adhere to and for the student to get support.
Studies show that students who received a video lecture separated into 28 manageable segments performed better than students who received a lecture containing the same information but with a significantly reduced number of segments. Therefore having 2 to 3 slides for 40 minutes knowledge nugget is not feasible.
The introduction of an audio presentation could be a good idea to add flexibility and digital inclusivity for the student. This was implemented in my Tort lecture where the presentation was given to be downloaded with a lecture explanation alongside. This meant I was able to listen to my lectures anywhere and added a high level of engagement and comprehension to my learning. Lastly, a clear font minimum of 12 with bold colors, and bullet points, avoiding italic and underlining with colored backgrounds with cream or yellow can be helpful to some SpLD students.
Gap 4: Digital Divide and Technology Access by Opeyemi Yusuf
The second issue covered was digital divide/technology access and gaps in an inclusive digital experience as a student at the University of Westminster. Digital divide can be defined as the gap between people who have access to modern information and communications technology and those who don’t. This technology includes laptops, computers, and access to quality internet.
A report by JISC found that 63% of students encounter problems with poor Wi-Fi connection, 30% with accessing online platforms and services and finally 24% struggle to pay for their mobile phone data. This highlights an issue within the University experience and student digital inclusivity.
Digital Divide and Technology Access Discussion
Firstly, there is a lack of check-in process in place to track student access to digital tools and technology such as laptops, right computer hardware or access to the internet. Moreover, digital tools such as the laptop safe unit have some disadvantages that prevent students from fully utilising these resources i.e, short-term loans are only available for MacBook devices and accessible only for 24 hours and long-term loans require approval for tutors to apply for them. There is a lack of funding in place to support students financially when they experience issues of low connectivity, wrong hardware and issues with technology devices. Lastly, the lack of awareness of the laptop safe units themselves i.e, Little Titchfield does not have a laptop safe unit.
Digital Divide and Technology Access Solution
Solutions to overcome Gap 4
Royal Northern College of music incorporated a system where at registration the college ask the students if they have access to the right hardware, appropriate study space and reliable internet connection for their studies at the college. This allows the college to track the resources available to the students and any problems students may encounter throughout the year and in turn, deliver an inclusive digital experience.
Solution regarding the laptop safe unit could be installing laptop safe unit on every campus. Campus such as Little Titchfield lack access to the laptop safe unit or the awareness of laptop loan service itself. I accidentally found the unit on the Marylebone campus while exploring, however it is difficult to imagine my classmates being aware of this.
In addition, poster prints around each university could also be distributed to raise awareness of digital tools and services available within the university. Finally, an improvement in the ease of access for long-term loans of laptops as most students tend not to contact their personal tutors while at university or increasing the duration of short-term laptop loans for the student. This means as a student I do not need to come in every 24 hours to access technology tools essential for my study. Overall, ensuring digital inclusivity and accessibility for all students.
Digital inclusivity tools currently available at the University of Westminster
Westminster Employability Award (WEA) 
WEA is an employability success award that formally recognises the extra- curricular activities you participate in during your term at the University of Westminster.
It contains several pre-arranged events for students to participate in and is intended to assist us in gaining work experience and developing critical abilities that companies are looking. By completing the Award, you will learn more about yourself, explore other possibilities, and become job- ready.
Upon successful completion of the Award, you will:
- Receive a digital badge for achieving a Bronze, Silver or Gold Award (can be shared on LinkedIn)
- Add something different to your CV and stand out from the crowd
- Gain confidence and be able to articulate your skills and experience to employers
- Attend the Vice-Chancellor’s Employability Awards celebration event.
- Get a chance to win one of the several financial prizes.
Digital inclusivity tools and subscriptions provided by the University of Westminster
POTENTIAL.LY 
- Personal and professional development platform which improves digital competency and online learning.
- Personality and career assessment tests, tutorials on how to use digital tools (Microsoft Office, LinkedIn, Teams, OneDrive etc) are available on it.
- Get badges to celebrate your accomplishments as well as points for the Westminster Employability Award.
ENGAGE AND ENGAGE+ 
- Careers and employability services team (CES) offers remote and in- person job opportunities, events and workshops for gaining work experience.
- CV, cover letter and interview advice, career guidance and simulators are also available.
- Build your own portfolio within the platform and gain points for the Westminster Employability Award
Reference/Citation Manager Software
Citation tools (also called bibliographic management tools or citation managers) help you organize, manage and format citations for your research. All of them have inbuilt pdf readers for your article and extract metadata to automatically prepare citations, which can be pasted onto your word document, rather than us having to manually type it out (Ivey and Crum, 2018).
ZOTERO – https://www.zotero.org/support
- Free (desktop and online web-based)
- supports a wide range of formats.
- no synced apps available.
- 300 MB of free storage
- can collaborate with many people.
MENDELEY – https://www.mendeley.com/guides
- Free (desktop and online web -based)
- supports only pdf formats
- synced apps also available.
- 2 GB of free storage.
- collaborate with only 2 or 3 members
REFWORKS – https://about.proquest.com/globalassets/proquest/files/pdf- files/userguide-refworks.pdf
- Free (online web-based only)
- supports only pdf formats.
- No synced apps available.
- 100 MB of free storage.
- collaborate with many members.
ENDNOTE – https://clarivate.libguides.com/endnote_training/users/enx9
- Paid (desktop and online web-based)
- Mostly supports pdf formats.
- synced apps available
- 2GB of storage
- can collaborate with other paid members.